BENGALURU: Researchers at the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) have developed an innovative solution to a persistent challenge in Mixed Reality (MR) technology for industrial applications: the need for extensive image datasets to train AI systems.
The team from IISc’s Department of Design and Manufacturing, led by Pradipta Biswas, has demonstrated that diffusion models — a specialised AI approach — can generate synthetic images that significantly improve object detection accuracy while dramatically reducing the need for real-world images.
“In recent years, MR technologies, where digital and physical elements are blended, are increasingly finding applications in manufacturing and maintenance industries. These systems often rely on AI to identify and interact with real-world objects,” IISc said.
However, it added, to train these AI models effectively, a large and diverse collection of images is needed.
Pointing out that gathering such real-world data can be expensive, time-consuming, and sometimes impossible in industrial settings due to safety or access restrictions, IISc said Biswas and team have found a creative solution: synthetic image generation.
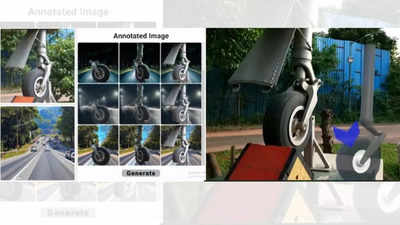
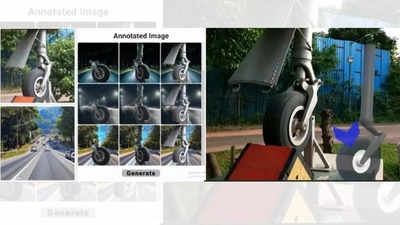
Instead of collecting thousands of real photographs, they used a special kind of AI approach, called a diffusion model, to generate realistic images.
They took images of real objects – such as parts of a pneumatic cylinder – and blended them with different background scenes where object detection has previously struggled. As per IISc, this helps the model “see” the object in a wide variety of settings, making it better at recognising the object in real life.
“The team tested this method against two other common techniques: traditional editing and GAN (Generative Adversarial Network). The diffusion-based approach led to much higher accuracy in detecting objects, even though it used fewer images. Specifically, it improved the detection performance by 11% while using 67% fewer images than the traditional methods,” IISc said.
Additionally, the team has created an easy-to-use interface so that others can generate their own synthetic data without deep technical knowledge, IISc said, adding that this makes it a powerful tool for improving machine learning models in MR applications where data is limited.